Brainwaves are rhythmic patterns of electrical activity that occur in the brain and can be measured using electroencephalography (EEG) technology. These brainwaves are produced by the synchronized electrical impulses of neurons firing in the brain.
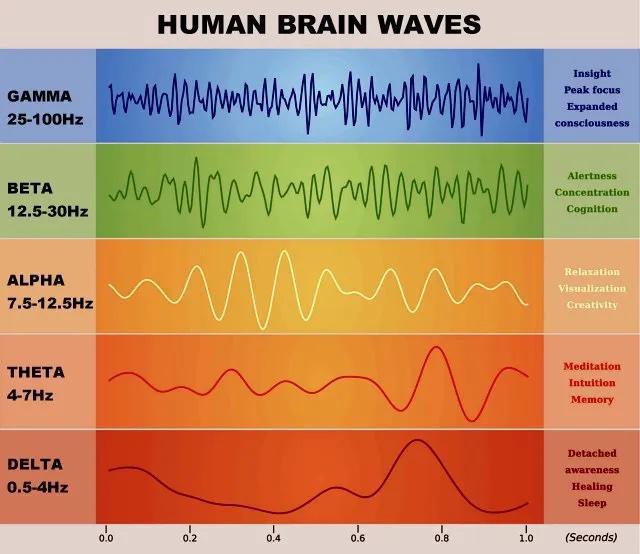
There are several different types of brainwaves, each associated with different states of consciousness, mental activity, and physiological functions. The five main types of brainwaves are:
Gamma Waves (30-100 Hz): Gamma waves are the fastest brainwaves and are associated with high-level cognitive functions such as problem-solving, learning, and information processing. They are also involved in states of heightened awareness and peak concentration.
Beta Waves (12-30 Hz): Beta waves are associated with active, alert, and focused mental activity. They are dominant during waking states and are often present when we are engaged in activities that require concentration, decision-making, and logical thinking.
Alpha Waves (8-12 Hz): Alpha waves are associated with a relaxed but alert state of mind. They are dominant when we are awake but in a calm and non-aroused state, such as during meditation, relaxation, or light daydreaming. Alpha waves are also associated with creativity and visualization.
Theta Waves (4-8 Hz): Theta waves are associated with deep relaxation, meditation, and the early stages of sleep. They are dominant during the transition between wakefulness and sleep, as well as during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. Theta waves are also associated with creativity, intuition, and spiritual experiences.
Delta Waves (0.5-4 Hz): Delta waves are the slowest brainwaves and are associated with deep, dreamless sleep and unconsciousness. They are dominant during deep sleep stages, and their presence is crucial for restorative sleep and physical healing.
Each type of brainwave serves a different purpose and plays a role in various aspects of cognition, emotion, behavior, and physiological functioning. The balance and synchronization of these brainwaves are essential for overall brain health and optimal functioning. Certain activities, practices, and interventions, such as meditation, mindfulness, biofeedback, and neurofeedback, can influence brainwave activity and promote states of relaxation, focus, and well-being.